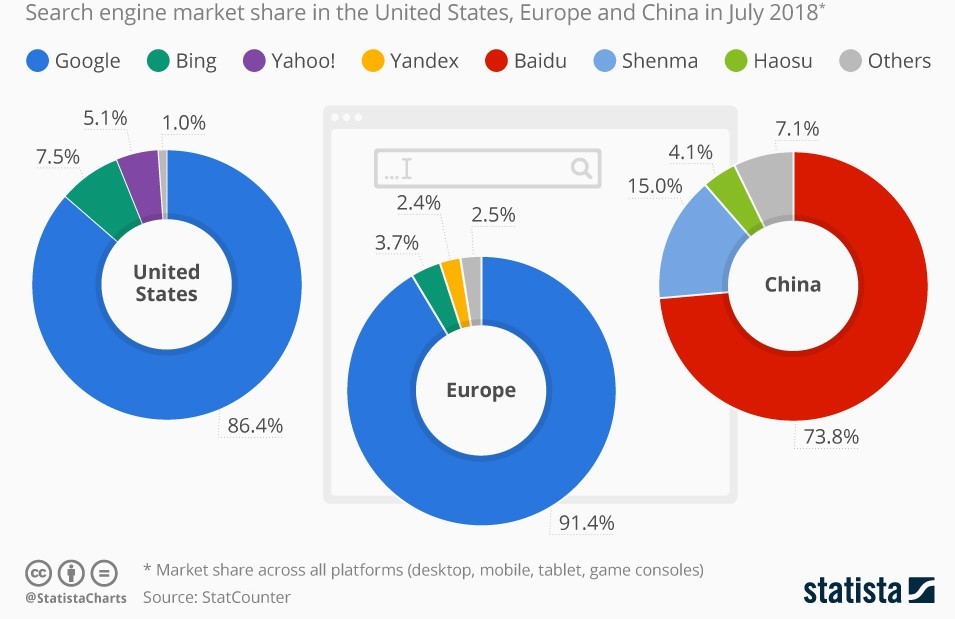
What is Baidu
Baidu was founded by Robin Li and Eric Xu in 2000. With 222 million users on Baidu in 2020, Baidu is a technology company most well-known for their search engine. Baidu is China’s biggest search engine that has the biggest index of Chinese web pages in the world and indeed is entirely Chinese-focused. The user interface is only available in Simplified Chinese language and offers a much higher priority to Chinese language sites.
Read on this full article to understand how you can rank better with the main SEO factors on Baidu to improve your organic ranking & conversion.
Differences in Baidu and Google’s Algorithm - Achieve Better Ranking Result
The easiest way to understand Baidu’s algorithm is that it abides by most of the same theoretical principles as Google’s, but is less effective in executing them in practice. So in a way, you can think of Baidu’s Algorithm as Google’s Algorithm with a 5-year lag.
Here are the summary key takeaways of some of these differences based on our experience and extensive research:
Localisation
There is a massive explicit preference towards anything Chinese in Baidu’s algorithm. Whether it’s server location, content-language, top-level domain (.cn), business address, backlinks, mentions, or citations — just about everything will be better for Baidu SEO if it’s from China or in Simplified Chinese.
It is very rare to see other websites with other languages than Chinese sites to rank high on Baidu for Chinese language queries. The queries based on many factors but mainly the user experience. The majority of Baidu users are residents of Mainland China, interested in local content in Chinese.
Likewise, one reason why foreign sites not hosted in China have difficulty ranking on Baidu is that connections and speeds to overseas servers from Mainland China can be very unreliable due to the Great Firewall. Baidu has an incentive to deliver results that load quickly and reliably for their users, so locally hosted content will often prevail.
Language Processing
By focusing on just one language, Baidu has gotten very sophisticated in parsing and understanding Chinese content. Baidu has a strong advantage over Google in Chinese natural language processing and typically provides more accurate results than any other search engine for Chinese queries.
Crawl Frequency
Baidu’s spider typically crawls Chinese sites more frequently than Google does. While crawling frequency depends on your website’s authority and update frequency, you can actually adjust Baidu’s crawl rate of your sites with Baidu Webmaster Tools (https://ziyuan.baidu.com/).
Penalties
Google’s system of handling penalties is much more robust than Baidu’s. In Google Search Console, website owners can view information about a site’s penalization and manual action status. They will typically process reconsideration requests much quicker as well. In Baidu, one penalization can often mean the death of the domain, as it can take years to recover lost rankings. Some speculate that this may be why negative SEO tends to be a relatively more common tactic in Baidu.
Content Freshness
Baidu favours websites that update content frequently. This is especially true for new websites. Just by frequently updating content very early on, sites may see improvement of overall rankings. Websites that aren’t updated for a few months may see a drop in rankings. We recommend publishing at least 1 piece of content each month, and to make sure you’ve submitted all of your website’s URLs to Baidu. Content freshness still matters for Google, but to a lower degree than Baidu.
Baidu Properties
For most of the sites, the biggest organic search competitor will be Baidu itself. That’s because, for almost all search queries, you can see at least one Baidu property (i.e. Baidu Zhidao, Zhihu, Baidu Baike, Baidu Tieba, etc) ranking among the top 5 positions. This by itself makes SEO on Baidu very different from Google.
Many believe that the Baidu algorithm gives more favour to their own properties. While this may seem obvious at first glance, it’s possible that Baidu’s claim that it does not favour its own properties is true. In the early days of the Chinese internet when there was far less high-quality content on the web, Baidu invested heavily in creating its own content hubs which quickly became very popular and attracted many backlinks. Therefore, it’s possible that Baidu’s dominance in organic search could be the result of deliberate manipulation, or simply that Baidu’s properties have accumulated so much content and links that they are now just impossible to beat.
Summary
To sum up, Baidu and Google might seem very similar but the deeper you explore, the more differences emerge. Baidu has more features and more ads crammed into their SERPs, with deep integration of their own product. However, their algorithm is simpler than Google’s in terms of determining page quality and has a strong preference for the Chinese. With the development of machine learning integrated into search engine algorithms, machine learning picks up on local user behaviour and search intent, cultural and behavioural differences of Chinese users will diverge Baidu even further from Google.