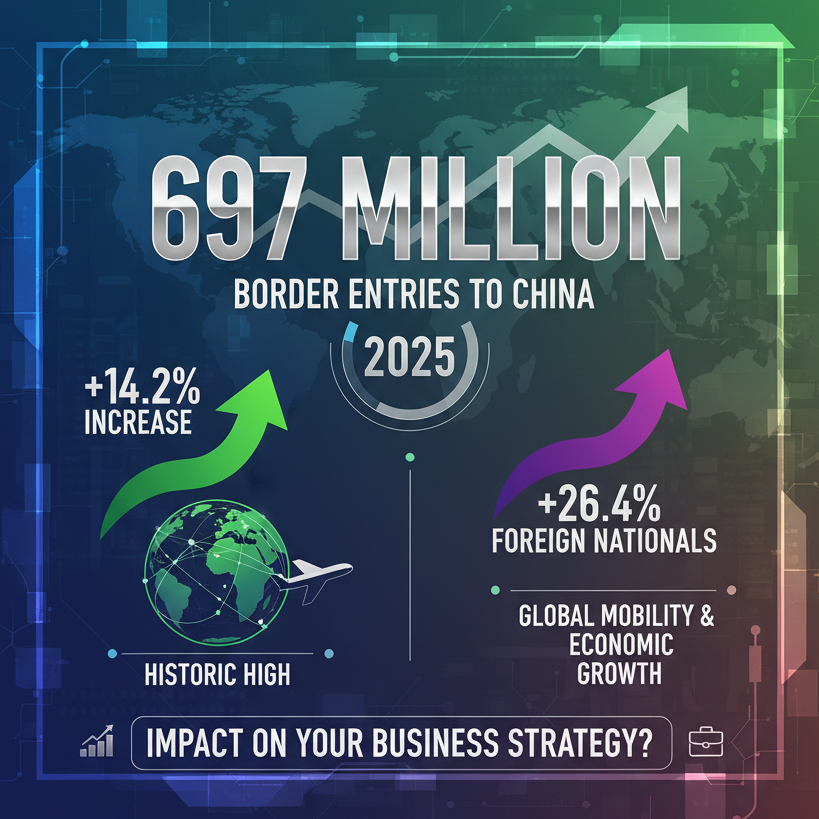
01. Owned media traffic
Owned media traffic refers to user clusters that enterprises can freely use without payment, can be reached at any time, and are deposited in relatively private channels such as their own apps, official accounts, personal WeChat, and WeChat groups.
02. Public domain traffic
Public domain traffic is a concept opposite to owned media traffic. In short, it is the traffic in a public area, and it is a platform shared by everyone, such as Weibo, TikTok, Xiaohongshu and other platforms.
03. Business domain traffic
Commercial domain traffic is the traffic that the platform draws from the public domain traffic and uses payment as the main distribution standard. In essence, commercial domain traffic is still public domain traffic, but the standard for allocating traffic has become payment-based. For example, TikTok news feed advertisements, etc.
04. Super User
First of all, super users must be heavy users of enterprise products and have a high demand for products; secondly, they have a clear willingness to continue to consume the products and services of the enterprise in the future, which is mainly reflected in their willingness to spend money. There are two key points in this definition, one is heavy users; the other is a clear willingness to continue to consume.
05.LTV (life time value)
It can be understood as the user's life cycle value, in simple terms: the whole process of the user from starting to contact the owned media until leaving. It can be divided into the introduction period, growth period, stable period, decline period, and loss period.
06. Growth market
A growth market refers to a potential market that has not been educated and seized by competitors.
07. User portrait
A simple understanding of user portraits is the labeling of user information. For example, users are categorized through information such as user age, gender, consumption habits, and region, so as to conduct a more targeted promotion or user management.
08. User stratification
User stratification is to establish a user label system, a user stratification system, and a stratified conversion strategy to achieve the purpose of refined user operation. It is also a method of labeling users.
09. User retention rate
This metric is used to measure the percentage of users who stay after a period of time. The retention rate calculation of the owned media community will generally track the retention of the next day, the retention of three days, the retention of seven days, and the retention of 30 days.
10. Five-step rule of owned media traffic operation
1) IP: Build a brand personality
2) Connection: Designing long-term value to attract user attention
3) Promotion: Create and maintain interactive exposure
4) Hierarchical: Establish user tags to achieve precise marketing
5) Repurchase: Guide user needs and creates secondary transactions
11. Touchpoint Marketing
A touchpoint is any point of interaction with a customer or potential customer at any stage of the customer journey.
12. User behavior path
User behavior path analysis is an analysis method that monitors the flow of users to measure product usage.
13. Pull
Pulling new users refers to pulling in new users, and the most direct indicator is the number of new users.
14. Activation/awakening
A simple understanding is to achieve the purpose of active users in some ways. Usually, users will be promoted in the community to make users pay attention to the brand again
15. Diversified
It is often used in advertising or content marketing. Different people can see different content through personalized tags and content recommendation systems, so as to achieve precise marketing.
16. SOP (Standard Operating Procedure)
The standard operating procedure is to describe the requirements of an event in a unified format to guide and standardize daily work.
17. Owned media fission
Owned media fission stimulates sharing based on owned media users and acquires new users through a social relationship chain.
18. Repurchase rate
The repurchase rate is a rate calculated based on the number of times consumers make repeated purchases of a product or service. The repurchase rate can reflect the loyalty of consumers to the product or service. The higher the rate, the higher the loyalty, and vice versa.
19. Conversion rate
Conversion rate refers to the ratio of the number of people who completed conversion behavior to the total number of people in the owned media within a statistical period. The calculation formula is: conversion rate = (converted people / total number of people) × 100%.
20. Owned media’s hourglass model
The hourglass pattern is a complete closed loop. From user attraction, user conversion, user retention, and user repurchase to sharing fission, it is a complete customer relationship management process. Only in this way can the company accumulate customers, make customers repurchase, and finally form a brand.
21. AARRR model
The AARRR model is one of the most common models in owned media traffic operations. The five processes of customer acquisition, activation, retention, realization, and dissemination, help merchants tap new traffic from the public domain and establish their own "owned media traffic pool".
22. RFM Model
RFM is a commonly used tool to measure user value. R (Recency) represents the interval between the customer's last transaction and the current time, F (Frequency) represents the customer's transaction frequency, and M (Monetary) represents the customer's transaction amount. Based on these three indicators, users can be divided into eight customer types, and corresponding measures can be taken according to different customer types to promote corporate decision-making.
23. Pareto Hierarchical Model
The Pareto model is also called the 28 law model, that is, 20% of users create 80% of the value of the enterprise, and operators need to spend 80% of their energy to serve 20% of high-quality users. It is often used for user stratification, so enterprises need to find this 20% of customers first and serve them well.
24. Blindspot
It is a common data collection method in data analysis. There are several methods of full embedding, code embedding, and visual embedding. Code embedding is divided into front-end embedding and back-end embedding.
25. A/B testing
A/B testing is often used in fission poster testing. In the same time dimension, in order to test the influence of a factor on the results, this factor is used as a variable, and other factors are quantitatively tested to find the variable scale with the best results.
26. Free membership
Users can acquire membership at no extra cost. This kind of membership model has a low threshold and wide coverage and is often designed as a "growth member" model. The most common one is the "points system". Different membership levels and benefits are distinguished according to your accumulated consumption behavior.
27. Paid membership
Users need to spend money to obtain membership, and it is limited time. This membership model has a high threshold and is mainly aimed at some users with high loyalty, high requirements, high repurchase, and high spending power. This can be subdivided into paid purchase consumption qualifications (such as Costco, Sam's Club, etc.), and paid purchase rights (such as Jingdong PLUS, Tmall 88VIP, etc.).
28. Stored value membership
The essence of "stored value membership" is a kind of pre-deposit behavior of consumption funds. The money is still the customer's, but it is stored on the merchant's side in advance, and I promise that it will be used for consumption in the future. The purpose of pre-deposit is to provide price concessions such as cashback, discount, etc., rather than paying additional premiums for certain rights or services.
29. Seed users
Such users are usually heavy users of the product, and are willing to give feedback and share to those around him. For example, brands communicate with torrent users through communities to tap demand, and they can better spread.
30. GMV (Gross Merchandise Volume)
That is, the total amount of commodity transactions, which means the total amount of transactions (within a certain period of time). For example, the monthly GMV of the community is 100,000 yuan.
31. ROI (Return on Investment)
It means return on investment, and the calculation formula is: return on investment (ROI) = profit / total investment × 100%.
32. DAU (Daily Active User)
The number of daily active users is often used to reflect the operation of websites, Internet applications, or online games. Websites are usually measured by daily UV, DAU is often used in apps, and WAU weekly activity and MAU monthly activity are common.
33. ARPU (average revenue per user)
Refers to the average revenue per user, an indicator used by operators to measure their revenue from each end user. When doing data analysis, ARPU generally refers to the customer unit price, but does not reflect the final profit margin.
34. API (Application Programming Interface)
An application programming interface that provides a set of routines that applications and developers can access based on a piece of software or hardware without having to access the source code or understand the details of the inner workings.
35. CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
Customer Relationship Management, which also usually stands for Customer Relationship Management System, is used by businesses to manage their relationships with customers.
36. SCRM (Social Customer Relationship Management)
That is social customer relationship management or customer relationship management based on social media.
37.ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
Enterprise resource planning refers to a management platform that is based on information technology, integrates information technology and advanced management ideas, and provides decision-making means for enterprise employees and decision-makers with systematic management ideas.
38. SaaS (Software-as-a-Service)
Software-as-a-Service, the service provided to the customer is the application program that the operator runs on the cloud computing infrastructure, and the user can access it through the client interface on various devices, such as a browser. Consumers do not need to manage or control any cloud computing infrastructure, including networks, servers, operating systems, storage, etc. It can be understood that they can be used by opening an account and password.
39.MCN (Multi-Channel Network)
The multi-channel network is a new mode of operation of the Internet celebrity economy. This model combines professional production content of different types and contents, and with the strong support of capital, ensures the continuous output of content, so as to finally realize the stable realization of business. At present, most of them are mining and incubating online celebrities, KOLs, and IP images, and designing development routes for them
40.PV (page view)
Page views are usually used as one of the main indicators to measure an online news channel or website or even a piece of online news.
41.UV (Unique Visitor)
Unique traffic refers to the number of people who visit a site or click on a news item from different IP addresses.
42. SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
Search engine marketing is a form of network marketing, which is a comprehensive and effective use of search engines for network marketing and promotion.
43. SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Use the rules of the search engine to improve the natural ranking of the website in the relevant search engines. The better the search engine optimization is, the higher the page ranking.
44. SMO (Social Media Optimization)
Social Media Optimization, is a comprehensive package of public communications through social media, online organizations and social networking sites.
45. KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
The key performance indicator method is one of the methods of enterprise performance appraisal.
46. OKR (Objectives and Key Results)
That is, the goal and key result method is a set of management tools and methods to clarify and track goals and their completion. KR (Key Results) is split through O (Objectives goals).
47.UGC (User Generated Content)
User-generated content means that users display or provide their original content to other users through the Internet platform. Zhihu can be said to be one of the most typical UGC platforms. The content is created by users, not the platform for users.
48.PGC (Professionally-generated Content)
Expert-created content is generally used to refer to the personalization of content, the diversification of perspectives, the democratization of communication, and the virtualization of social relations.
49. LBS (Location Based Services)
Location-based services use various types of positioning technologies to obtain the current location of the positioning device and provide information resources and basic services to the positioning device through the mobile Internet.
50.MOT (Moment of Truths)
MOT is a key indicator and a specific measurement of customer orientation because customers will only remember those critical moments to help companies implement the user-centric concept.
51. ASO optimization
App store optimization is to make APP easier to be searched or seen by users by using the search rules and ranking rules of the App Store.
52. Rich Media
That is, the English literal translation of Rich Media itself is not a specific form of Internet media, but refers to information dissemination methods with animation, sound, video, or interactivity.
53. Search Ads
The most typical is Baidu's bidding advertising. Merchants bid to buy keywords. When the content of the user's search triggers the keyword, the corresponding advertisement is displayed in the search list.
54. Display ads
Banner and other advertising spaces on information websites are all display advertisements. For example, the image advertisement at the bottom of the WeChat official account
55. Open screen advertisement
After most apps are launched, they will see a full-screen advertisement, and the display time varies from 3-5 seconds such as Zhihu, Douban, Xiaohongshu, etc.
56. News Feed Ads
Advertisements are inserted into the information list in the form of articles, pictures, videos, etc.
57. Video Ads
On video sites such as iQiyi, Youku, and Tencent Video, when we do not purchase memberships, advertisements appear before the video, during the playback, and during the pause.
58. Common types of communities
Pop-out group: temporarily gather a group of people and disband immediately after the end
Selling group: for the purpose of quick sales
Activity group: for the purpose of pulling new members
59. North Star Indicator
North Star Metric, also known as One Metric That Matters, refers to the absolute core metrics related to business/strategy at the current stage of the product. Once established, it shines in the air like the North Star, guiding The team is moving in the same direction (improving this metric).
60. KOL: Key Opinion Leader
People who have accurate product information, are trusted by relevant groups, and have greater influence on the purchase behavior of this group are generally transformed from PGC and OGC.
61. KOC: Key Opinion Consumer
Someone who can make convincing evaluations or experiences of related products, and can drive other potential consumers to make purchases.
62. Big V
Refers to the celebrity account with the head of the fan group in a certain field.
63. Amateur
Ordinary netizens who have a certain aesthetic and network sense and are active in a certain platform and love to share.
64.PR
Refers to the brand public relations position, responsible for brand promotion, formulating publicity strategies, communication and negotiation with media such as celebrities.
65. VLOG
Vlog is a type of blog, the full name is video blog or video log, which means video recording, video blog, video network log.
66. Subscription number
To provide users with information, most accounts can push up to 8 messages at a time daily, displayed in the "Subscription Accounts" folder.
67. Service Account
It mainly provides services for users, pushes four times a month, with a maximum of 8 messages each time, displayed on the home page of the chat list, and can apply for a custom menu.
68. Whitelist
Open a whitelist for the WeChat public account and authorize the other party to share your own original articles.
69. Single tick
When others share your own articles, you can choose "shared articles can be modified" and "shared articles can not show the source", just click "can be modified" is a single check.
70. Double check
Referring to the definition of a single check, if both are checked, it is a double check.
71. Open Rate
The open rate is the rate at which fans open an article through an official account conversation.
72. Long tail traffic
An article that getting a steady stream of traffic both in the early and late stages, has a long tail effect.
73. Advertiser & Traffic Master
The official account can be opened as an advertiser, that is, you can promote and introduce yourself in other people's official accounts to achieve the purpose of attracting traffic. After the fans of the official account reach a certain level, you can open a traffic master, that is, help others to advertise where you can get monthly advertising revenue.
74.TP
TP (Time On Page) refers to the length of time a user stays on each page. TP duration can reflect the attractiveness of a web page or activity page to users.
75. PR value
The full name is Pagerank (page level), which is a method for evaluating the "importance" of a webpage.
76. Reptiles
Also known as a web spider, it is a program or technology that automatically crawls Internet information according to certain rules.
77. Links
Also known as website exchange link, it is a simple form of cooperation between websites with certain complementary advantages of resources.
78. Three common models of user psychology
Psychology of scarcity: When we think we lack something, we may be obsessed with it, so this scarcity will exist in the subconscious, and it is easy to generate a series of strong needs in our brains.
Loss aversion mentality: When faced with the same amount of gain and loss, people will feel that loss is more difficult to accept than gain. For example, the sense of loss that you lose 100 yuan is far greater than the joy you feel that you earn 100 yuan.
Primacy effect: It can be understood that when consumers first come into contact with a brand or product information, they will form a stable and lasting impression of the brand or product.
79. AIPL model
The AIPL model is the journey from cognition to loyalty of consumers, AIPL means cognition, interest, purchase and loyalty respectively.
80. K value model
Number of new users invited/number of users actively invited. The K value is the number of new users that each user can bring. The larger the K value, the better the propagation effect.
81. User research practice model
"1000/100/10" rule check the feedback of 1,000 users in the forum and reply, follow 100 users, and do 10 user research every month.
82. Grayscale test
If the software will launch a new function or make a major revision, it is necessary to try work in a small area first, and then slowly increase the volume until the new function covers all system users.
83.5W1H
Also known as the six-point analysis method which refers to the reason (Why), object (What), location (Where), time (When), personnel (Who), and method (How) that raise questions for consideration.
84. PDCA review model
This model is the ideological and methodological basis of the total quality management that Deming tried his best to promote. The PDCA model not only be applied to quality management, but it is also very efficient to review at the individual level. The PDCA model is divided into 4 stages: Plan (planning), Do (execution), Check (check), Act (processing).
85. Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is a form of graph that relates activities to time, showing how long each activity lasted. The Gantt chart can track the progress as a whole, and clearly identify the start and end time of each task.
86.WBS task decomposition method
The task decomposition method is also called Work Breakdown Structure, or "WBS" for short, which is to decompose complex and abstract tasks into specific, executable, and operable items, and then break them down one by one and complete them one by one.
87. SWOT Analysis
This model is mainly a method to summarize the research results by analyzing the strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and challenges existing inside and outside the enterprise. From 4 aspects: Strength (advantage), Weakness (disadvantage), Opportunity (opportunity), Threat (challenge).
88. STAR Act
The STAR rule is a tool that can be used in a variety of scenarios to collect and organize relevant information which includes Situation (scenario), Task (task), Action (action), Result (result).
89. SMART principle
S (Specific clarity), M (Measurable), A (Attainable), R (Relevant), T (Time-based timeliness). This principle is to help employees work more clearly and efficiently, and it also provides assessment objectives and assessment standards for managers to implement performance assessments for employees in the future, making assessments more scientific and standardized.
90. RACI Responsibility Allocation Matrix
RACI is a relatively intuitive model for identifying roles and their associated responsibilities in an organizational change process. RACI clearly indicates the relationship, responsibilities and status in the organization which is very conducive to the smooth progress of the project. RACI stands for (R = Responsible), (A = Accountable), (C = Consulted), and (I = Informed).
91. Digitization
In most cases, digitalization in business refers to the improvement of business processes, business functions, business operations, etc. by leveraging new technologies provided by the digital space. It allows new systems to be built in the context of digitization, making it easier for the business and realizing any/all benefits that the business may consider.
92. PaaS
PAAS (Platform as a Service) platform as a service. A business model that provides server platforms as a service. Such as Alibaba Cloud and Baidu Cloud.
93. Omni-channel
Omni-channel such as online APP, mall, applet, e-commerce platform, offline store, POS system, etc. In short, it is all the scenarios that consumers may appear in.
94. CDP
CDP is an enterprise customer information database managed by marketers. This database connects consumer information in different departments and systems in a unified manner.
95. DMP
Data Management Platform integrates scattered multi-party data into a unified technology platform, and standardizes and subdivides these data, so that users can push these subdivision results into the existing interactive marketing environment. platform.
96. Data Center
The data middle platform refers to the collection, calculation, storage, and processing of large amounts of data through data technology, while unifying standards. After unifying the data, the data center will form standard data, and then store it to form a big data production layer to provide customers with efficient services.
97. Data Silos
To put it simply, "data island" refers to the closed, semi-closed, semi-closed, redundant, asymmetrical, redundant, and so on due to the initiative of the subject, the technicality of the object, and the incompleteness of the policy environment and system construction during the formation, analysis, and use of data and data sets. closed phenomenon.
98.OneID
Literally means "one identity recognition", through the OneID system to complete the identification of customers, channels, products and other business objects and data connection, to solve the problem of data islands.
99.UID
UID is the short form for User Identification, which is a value automatically generated by the system when the online platform is registered.
100. RPA
RPA is a software automation technology that usually runs on the computers of office workers in the form of "software", sometimes referred to as "RPA robots."